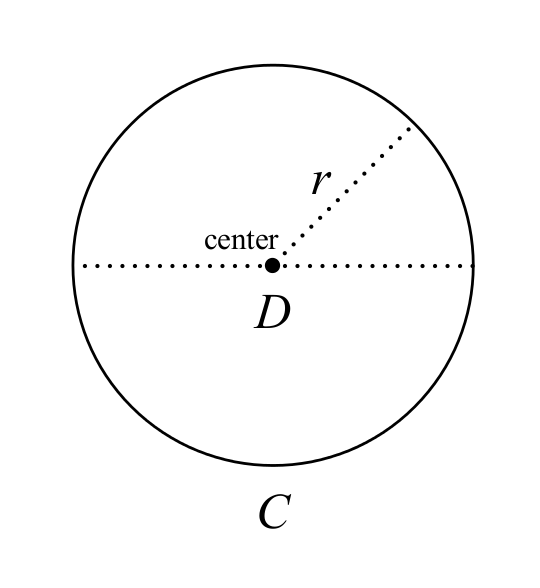
Circle on a Graph Let us put a circle of radius 5 on a graph Now let's work out exactly where all the points are We make a rightangled triangle And then use Pythagoras x 2 y 2 = 5 2 There are an infinite number of those points, here are some examples(x 5) ^ 2 (y 8) ^ 2 = 18 forma standard di un cerchio è (x a) ^ 2 (y b) ^ 2 = r ^ 2 dove (a, b) è il centro del cerchio e r = raggio in questa domanda il centro è noto ma r non lo è Per trovare r, tuttavia, la distanza dal centro al punto (2, 5) è il raggio Usando la formula della distanza ci permetterà di trovare in effetti r ^ 2 r ^ 2 = (x_2 x_1) ^ 2 (y_2 y_1) ^ 2(y − 8)2 9 = 1 Graph each equation 9) x2 4 y2 9 = 1 x y −8 −6 −4 −2 2 4 6 8 −8 −6 −4 −2 2 4 6 8 10) x2 49 y2 = 1 x y −8 −6 −4 −2 2 4 6 8 −8 −6 −4 −2 2 4 6 ©W U2x0 z1r1 R fK 3uxt rai DSGoUfbtZw va 8rpe Y yLKL SCAq 9 Slwlm ArIi5glh utksj Arue1sFecr 7vVeQd77 u GMZaxdnek xw2iKtlha uI RnLftilnRigt 2e7

Droidscript In Every Field
Formula cerchio x^2+y^2
Formula cerchio x^2+y^2-Ci sono 2 punti di introspezione A = ( 4;9x 2 16y 2 − 36x − 64y 44 = 0 A) C) B) D) ____ 18 Write the equation of the ellipse that has its center at the origin with focus at (0, 4) and vertex at (0, 7) A) x 2 49 y 2 33 = 1 C) x 2 33 y 2 49 = −1 B) x 2 33 − y 2 49 = 1 D) x 2 33 y 2 49 = 1 ____ 19 Find the center and vertices of the ellipse x2 9y2 16x− 54y




Mohr S Circle Wikipedia
Y xTy st jjyjj 2 1 CauchySchwarz implies that xTy jjxjjjjyjj jjxjj and y= x jjxjj achieves this bound Proof of (3) We have jjxjj 1 =max y xTy st jjyjj 1 1 So y opt= sign(x) and the optimal value is jjxjj 1 2 Positive semide nite matrices We denote by S n the set of all symmetric (real) n nmatricesOtterrai finalmente x = rcos theta e Y = r sin theta Applicando il teorema di Pitagora, otterrai x ^ 2 y ^ 2 = r ^ 2 Vale a dire l'equazione di un cerchio che ha il centro all'origine Puoi anche trovare l'equazione generale usando questo metodo O puoi usare l'algebra vettoriale per trovare l'equazione di un cerchioIn algebra, a quadratic equation (from the Latin quadratus for "square") is any equation that can be rearranged in standard form as ax²bxc=0 where x represents an unknown, and a, b, and c represent known numbers, where a ≠ 0 If a = 0, then the equation
3) e B = (3;WolframAlpha is capable of solving a wide variety of systems of equations It can solve systems of linear equations or systems involving nonlinear equations, and it can search specifically for integer solutions or solutions over another domain Additionally, it can solve systems involving inequalities and more general constraintsQuesto strumento è in grado di fornire Raggio del cerchio dato il centro (h, k) e il punto (x, y) calcolo con le formule associate ad esso
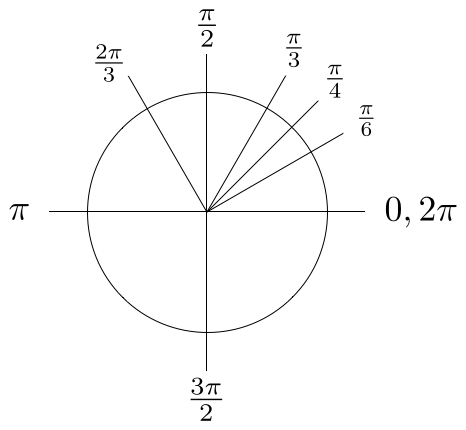
Si tratta di un cerchio centrato in un punto P (4, 2) con un raggio di 3 Quindi, inserire l'equazione così com'è oppure estrarre una bussola, individuare il centro su carta millimetrata, impostare la bussola su 3 cm e disegnare graph {(x 4) ^ 2 (y2) ^ 2 = 9 92, 4124, 112, 5454}Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, historyPythagoras Pythagoras' Theorem says that for a right angled triangle, the square of the long side equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides x 2 y 2 = 1 2 But 1 2 is just 1, so x 2 y 2 = 1 (the equation of the unit circle) Also, since x=cos and y=sin, we get (cos(θ)) 2 (sin(θ)) 2 = 1 a useful "identity" Important Angles 30°, 45° and 60° You should try to remember




Agonism Antagonism And Inverse Agonism Bias At The Ghrelin Receptor Signaling Journal Of Biological Chemistry




X 2 Y 2 Formula X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Xy Yz Zx Formula Luar Biasa
INTEGRALI DOPPI Esercizi svolti SOLUZIONI 1 Calcolare i seguenti integrali doppi (a) Z A xy dxdy, A = {(x,y) 0 ≤ x ≤ 1,0 ≤ y ≤ 1} E possibile risolvere l'integrale indifferentemente per orizzontali oConsider x^ {2}y^ {2}xy22xy as a polynomial over variable x Find one factor of the form x^ {k}m, where x^ {k} divides the monomial with the highest power x^ {2} and m divides the constant factor y^ {2}y2 One such factor is xy1 Factor the polynomial by dividing it by this factorPartial Differential Equations Igor Yanovsky, 05 2 Disclaimer This handbook is intended to assist graduate students with qualifying examination preparation




Circonferenza In Enciclopedia Della Matematica




Droidscript In Every Field
Given x2 (y −2)2 = 4 Here is a graph of the original equation Expand the square x2 y2 − 4y 4 = 4 Use r2 = x2 y2 and y = rsin(θ) to convert r2 −4rsin(θ) 4 = 4 Combine like terms r2 −4rsin(θ) = 0 We can discard a common factor of r, because it is only the trivial root r = 0After you enter the expression, Algebra Calculator will plug x=6 in for the equation 2x3=15 2(6)3 = 15 The calculator prints "True" to let you know that the answer is right More Examples Here are more examples of how to check your answers with Algebra Calculator Feel free to try them now For x6=2x3, check (correct) solution x=3 x6=2x 6 Cosa hanno a che fare i coni con le quadratiche?




A Review Of Big Data Analysis Methods For Baleen Whale Passive Acoustic Monitoring Kowarski 21 Marine Mammal Science Wiley Online Library




Math Linear Mathematics Education Circle Background With Geometrical Plots Formulas And Calculations Design Concept Vector Illustration Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image
72 CALCULUS OF VARIATIONS c 06 Gilbert Strang If this energy has its minimum at u(x;y), then P(u v) P(u) for every v(x;y) We mentally substituteCircle equation calculator 1 Input circle equation in standard or in general form 2 You can input integers ( 10 ), decimals ( 102 ), fractions ( 10/3) and Square Roots (use letter 'r' as a square root symbol) Example 2r3 = 2 ⋅ 3 = 0 NOTE To input square root1 Dimostrare che la differenza nell'area del circumcircle e del poligono è maggiore della differenza nell'area del poligono e dell'incircle;



Hal Archives Ouvertes Fr Hal Document



Is Cetirizine A Sulfa Drug Order Generic Online Without
Factor x^2y^2 x2 − y2 x 2 y 2 Since both terms are perfect squares, factor using the difference of squares formula, a2 −b2 = (ab)(a−b) a 2 b 2 = (a b) (a b) where a = x a = x and b = y b = y (xy)(x−y) (x y) (x y)$\begingroup$ Hi @Marc First note that for any pair of rational points we can connect them with a line which has a rational (or undefined) slope Second note that the pointFormula (111) del testo può essere posta nella forma Ia xi ya y y x 2 3 h G x 0 h h 3 b 6 Momento d'inerzia polare rispetto al vertice di un triangolo Volume 1 Capitolo 11 Paragrafo 2 5 distante y dal centro O del cerchio, la sua area è da = 2π y dy, e il momento 72 Finding Volume Using Cross Sections Warm Up Find the area of the following figures 1 A square with sides of length x 2 A square with diagonals of length x 3 A semicircle of radius x 4 A semicircle of diameter x 5 An equilateral triangle with sides of length x 6 An isosceles right triangle with legs of length x




A Review Of Big Data Analysis Methods For Baleen Whale Passive Acoustic Monitoring Kowarski 21 Marine Mammal Science Wiley Online Library



Page 7 9 Cos High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
The curve with equation y = x2 cos has stationary point at x = p in the interval 0 < x < π i) Show that p satisfies the equation tan = 3 ii) Verify by calculation that p lies between 2 and 25 2 iii) Use the iterative formula p n1 = 2 tan 1 ( ) to determine the value of p correct toMohr's circle is a twodimensional graphical representation of the transformation law for the Cauchy stress tensor Mohr's circle is often used in calculations relating to mechanical engineering for materials' strength, geotechnical engineering for strength of soils, and structural engineering for strength of built structures It is also used for calculating stresses in many planes by4 n 2 n 1 c n 2 xn y y y y 2c 2 2 3c 3 x n 2 3 n n 1 c n xn 2 y c 1 2c 2 x 3c 3 x2 n 1 nc n xn 1 y c 0 c 1 x c 2 x2 c 3 x3 n 0 2 c n xn y y 0 y y 0 c 0, c 1, c 2, y f x n 0 c n xn c 0 c 1 x c 2 x2 c 3 x3 1 y 2xy y 0 1 By writing out the first few terms of (4), you can see that it is the same as (3) To obtain (4) we replaced by and




How To Find The Circumference And Area Of A Circle 14 Steps




Compute The Area Of Intersection Between A Circle And A Triangle Stack Overflow
The standard form of the equation of an ellipse with center (0,0) ( 0, 0) and major axis parallel to the y axis is x2 b2 y2 a2 =1 x 2 b 2 y 2 a 2 = 1 where a >b a > b the length of the major axis is 2a 2 a the coordinates of the vertices are (0,±a) ( 0, ± a) the length of the minor axis is 2b 2 bSimilarly, if we are given an equation of the form y 2 AyBxC=0, we complete the square on the y terms and rewrite in the form (yk) 2 =4p(xh)From this, we should be able to recognize the coordinates of the vertex and the focus as well as the equation of the directrix I am going to develop a 2d ball game where two balls (circles) collide Now I have the problem with determining the colliding point (in fact, determining whether they are colliding in xaxis/y
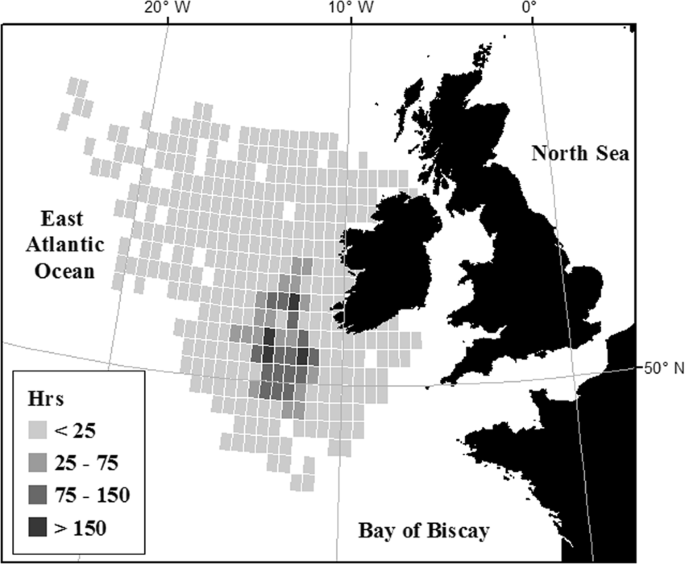



Seismic Surveys Reduce Cetacean Sightings Across A Large Marine Ecosystem Scientific Reports




Federal Register Takes Of Marine Mammals Incidental To Specified Activities Taking Marine Mammals Incidental To Geophysical Surveys In The Atlantic Ocean
Formula cerchio x^2 y^2 3364Formula cerchio x^2y^2 In mathematics, trigonometric substitution is the substitution of trigonometric functions for other expressions In calculus, trigonometric substitution is a technique for evaluating integralsMoreover,2) If c > 0, the graph of xy = x y c crosses the yaxis at (c);4) Per trovare se ci sono dei punti di intersezione devi risolvere un sistema di equazioni che includa le equazioni di circonferenza e di linea {(x ^ 2 y ^ 2 = 25), (y = x 1)} Se sostituisci x 1 per y nella prima equazione ottieni x ^ 2 (x 1) ^ 2 = 25 x ^ 2 x ^ 2 2x 1 = 25 2x ^ 2 2x24 = 0 Ora puoi dividere entrambi




Equazione Della Circonferenza Per Superiori Redooc
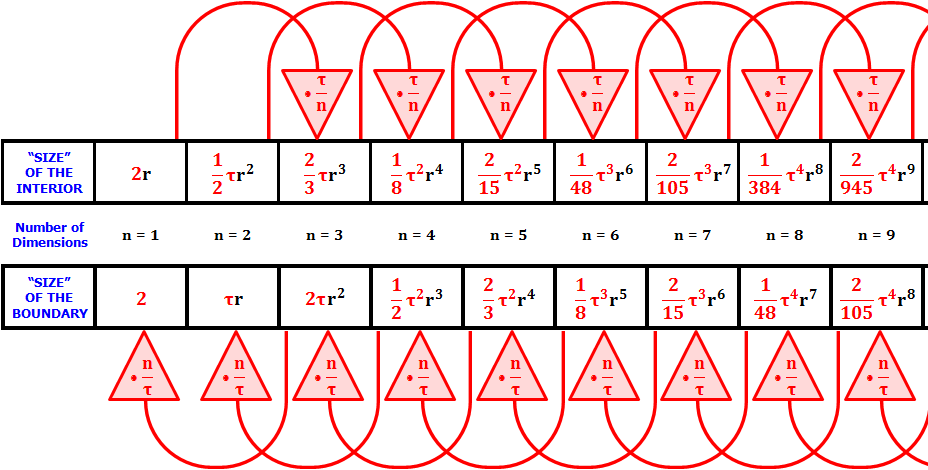



Tau Day No Really Pi Is Wrong The Tau Manifesto By Michael Hartl
1 Dimostra che la somma dei raggi dei cerchi ;Sostituisci h con la coordinata x del centro, k con la coordinata y e r con il raggio del cerchio Ad esempio, con un'origine di (2, 3) e un raggio di 5, l'equazione diventa (x ( 2)) ^ 2 (y 3) ^ 2 = 5 ^ 2, che è anche (x 2) ^ 2 (y 3) ^ 2 = 5 ^ 2, poiché la sottrazione di un numero negativo ha lo stesso effetto dell'aggiunta diCerchio e circonferenza in Geometria sono rispettivamente la parte di piano delimitata dalla circonferenza e l'insieme dei punti equidistanti da un punto fissato, detto centro del cerchioLa distanza dei punti della circonferenza dal centro viene detta raggio Questo formulario è interamente dedicato a circonferenza e cerchio



Estimating Sampling Selection Bias In Human Genetics A Phenomenological Approach




Equazione Della Circonferenza
Y er2t 2 = Therefore, a general solution of (*) is y Cy C y Cer1t Cer2t = 1 1 2 2 = 1 2 It is that easy Example y″ 5 y′ 4 y = 0 The characteristic equation is r2 5 r 4 = (r 1)(r 4) = 0, the roots of the polynomial are r = −1 and −4 The general solution is then y = C1 e −t C 2 e −4tThe Gaussian integral, also known as the Euler–Poisson integral, is the integral of the Gaussian function = over the entire real line Named after the German mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss, the integral is = Abraham de Moivre originally discovered this type of integral in 1733, while Gauss published the precise integral in 1809 The integral has a wide range of applications Poiché la linea "tocca" il cerchio, c'è solo un punto di intersezione con il cerchio Pertanto, l'equazione, $$ x^2(2x5)^216x12(2x5)c=0 \implies 5 x^2 60 x




O9fthe70oykalm



2
A sphere is the graph of an equation of the form x 2 y 2 z 2 = p 2 for some real number p The radius of the sphere is p (see the figure below) Ellipsoids are the graphs of equations of the form ax 2 by 2 cz 2 = p 2, where a, b, and c are all positive1 Trovare la forma standard dell'equazione della parabola chiusaAbbiamo i due cerchi x ^ 2 y ^ 2 = 9 (1) e x ^ 2 y ^ 2 2ax 2y 1 = 0 (2) L'equazione del primo cerchio ci dice che il suo centro è a (0, 0) e ha un raggio di 3 L'equazione del secondo cerchio ci dice che il suo centro è situato a (a, 1) Ciò si ottiene come segue x ^ 2 2ax y ^ 2 2y = 1 Competi i quadrati sull




Equazione Della Circonferenza
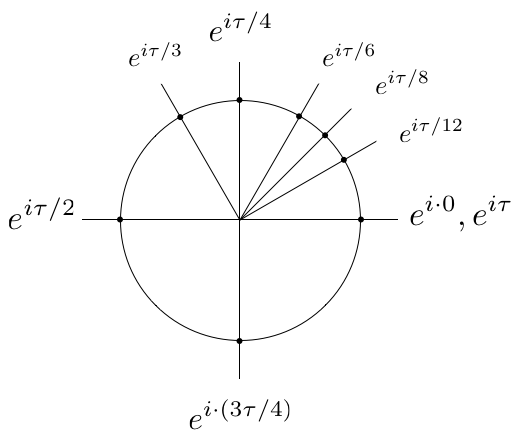



Tau Day No Really Pi Is Wrong The Tau Manifesto By Michael Hartl
Combining (245) and (247), we reach au x bu y = c (248) which ends the proof 213 A word on fully nonlinear equations The equation a(x,y,u) u x b(x,y,u) u y = c(x,y,u) (249) is called "quasilinear" because it is linear with regard to the highest order derivatives uFormule della circonferenza Le formule per la circonferenza nel piano cartesiano riprendono ed ampliano le formule per cerchio e circonferenza già note dallo studio della Geometria Euclidea, per cui è bene ricordarle tutte in modo da risolvere agevolmente gli esercizi e iPerché 2 è speciale?



Page 7 9 Cos High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Divine Grace And The Remedy Of The Imperfect People
La forma standard dell'equazione del cerchio sarebbe (x 3) ^ 2 (y 2) ^ 2 = 9 La forma standard dell'equazione di un cerchio è (x x_1) ^ 2 (y y_1) ^ 2 = r ^ 2 xey sono le variabili x e y, x_1 è la coordinata x del centro, y_1 è la coordinata y del centro e r il raggio del cerchio Per posizionare il centro del cerchio nel punto (3, 2), basta sostituire x_1 con 3 e y_1 con 2We will find all the solutions to the equation x^2=2^x as many of you guys have We will find all the solutions to the equation x^2=2^x as many of you guys have been asking Lecture onThese graphs, as the ones before, are also asymptotic to the lines y = 1 and x = 1 At this point, it is possible to make several conjectures 1) the graph of the equation xy = x y c is a hyperbola asymptotic to y = 1 and x = 1;



Calcolo Coordinate Punti Di Contatto Tra Parabola Asse Verticale E Circonferenza



Cerchio Wikipedia



1




Equazione Della Circonferenza E Formule Del Piano Cartesiano Coniche Weschool




Bookflare Net An Introduction To The History Of Algebra Solving Equations From Mesopotamian Times To The Renaissance Pdf Cuneiform Equations



Hal Archives Ouvertes Fr Hal Document




Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Sibo




Pdf Validation Of Three Predictive Equations For Basal Metabolic Rate In Adults




Circonferenza In Enciclopedia Della Matematica




Find The Point On A Circle With Given Center Point Radius And Degree Stack Overflow
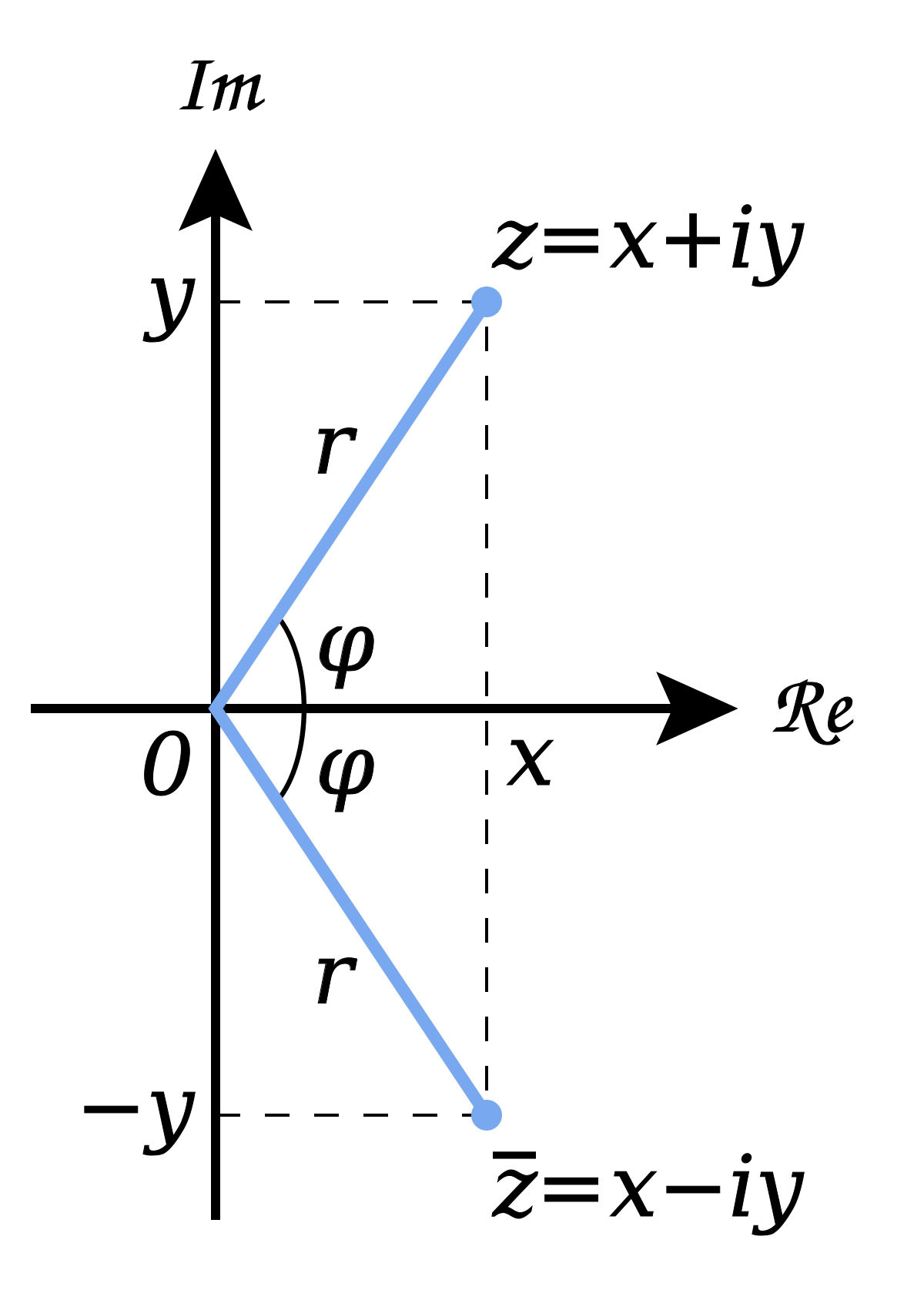



Complex Plane Wikipedia




Can All Circles Of Radius 1 N Be Packed In A Unit Disk Excluding The Circle Of Radius 1 1 Newbedev




Ptn Pepi S Tire Noodle Photos Facebook




Can All Circles Of Radius 1 N Be Packed In A Unit Disk Excluding The Circle Of Radius 1 1 Newbedev



La Circonferenza Come Calcolare Il Raggio E Le Coordinate Del Centro Mediante Equazioni E Formule Weschool



View Of Sph Boundary Deficiency Correction For Improved Boundary Conditions At Deformable Surfaces Ciencia Y Tecnologia De Buques




3 Ways To Calculate The Diameter Of A Circle Wikihow



Equation Of A Circle




Equazione Della Circonferenza E Formule Del Piano Cartesiano Coniche Weschool
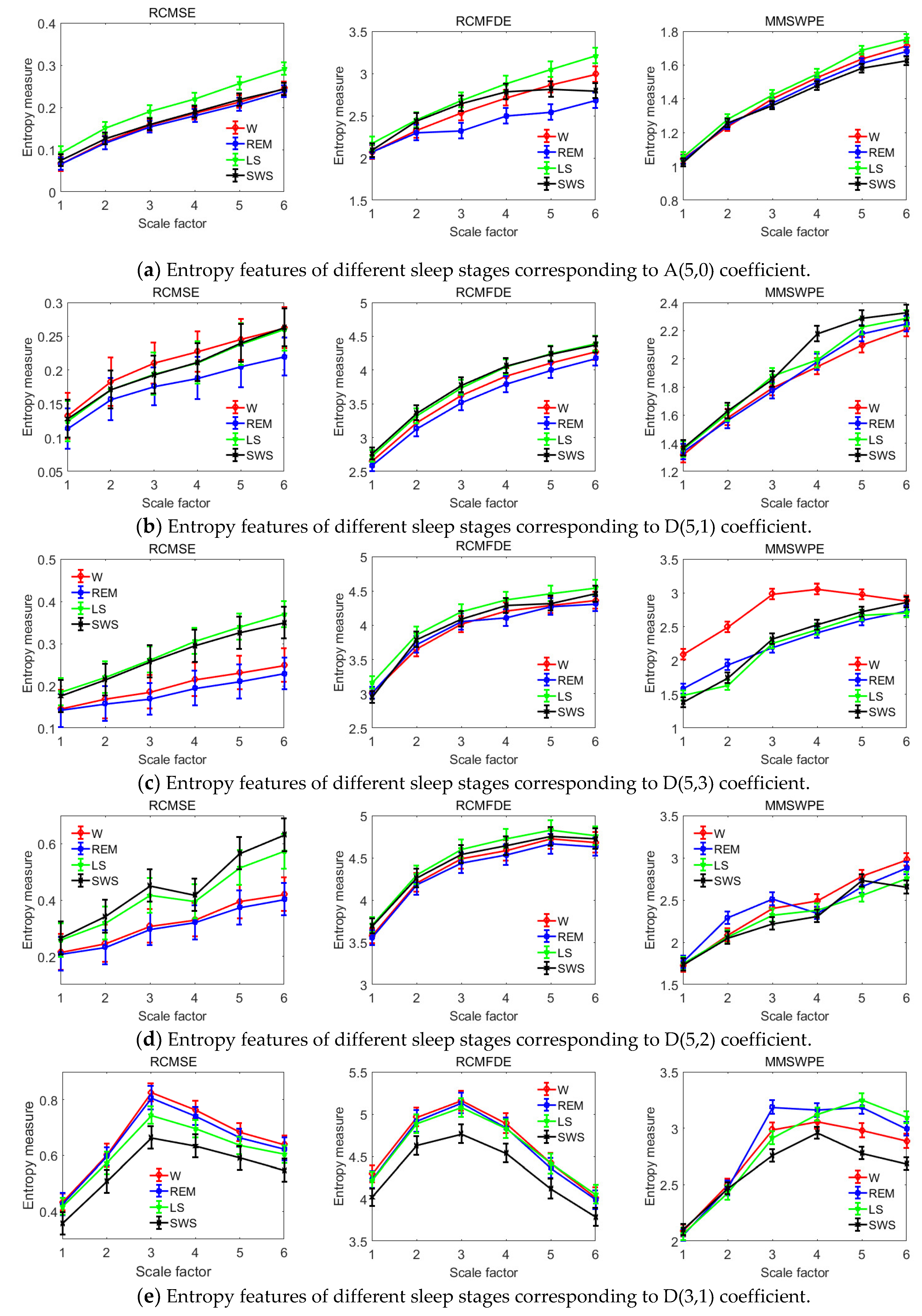



Entropy Free Full Text A Novel Microwave Treatment For Sleep Disorders And Classification Of Sleep Stages Using Multi Scale Entropy Html




Circonferenza




009 Mcmicrocomputer Vebuka Com



Q Tbn And9gcsmc1dwpbrc6yjadmhvjqer8bj3bgkdpwkjaijncxzd1b3y7iza Usqp Cau



Circle Disk Segment Sector Formulas Characterizations And Properties Of A Circle




Pixel Circle Oval Generator Minecraft Donat Studios




Planetside 2 Logo Decals By Nostalgianights Community Gran Turismo Sport




Thehoop 30 Aerial Hoops 30 Mm Agm Design Shop



Hal Archives Ouvertes Fr Hal Document



Sustainability Free Full Text Regulatory Elements On The Circular Economy Driving Into The Agri Food System Html




Circonferenza




Formule Del Cerchio Scuolissima Com



Tau Day No Really Pi Is Wrong The Tau Manifesto By Michael Hartl




Mohr S Circle Wikipedia



Calcolo Coordinate Punti Di Contatto Tra Parabola Asse Verticale E Circonferenza




Agonism Antagonism And Inverse Agonism Bias At The Ghrelin Receptor Signaling Journal Of Biological Chemistry




3 Ways To Calculate The Diameter Of A Circle Wikihow



2




La Circonferenza Nel Piano Cartesiano Ppt Scaricare



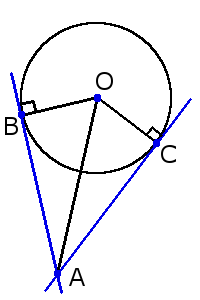
Le Rette Tangenti Condotte Da Un Punto P Ad Una Circonferenza Possono Essere O Due O Una Sola A Seconda Se Il Punto P E Estern




Bioinformatica Paolo Maccallini




A Generalized Power Law Detection Algorithm For Humpback Whale Vocalizations The Journal Of The Acoustical Society Of America Vol 131 No 4



Circle Wikipedia



1



Equation Of A Circle




Equilibrium Line An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Tau Day No Really Pi Is Wrong The Tau Manifesto By Michael Hartl



Miky Genny Geometria Circonferenza E Complementi



X 2 Y 2 Formula X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Xy Yz Zx Formula Luar Biasa




Pdf Error Bounds For Asymptotic Solutions Of Second Order Linear Difference Equations Ii The First Case



Calcolo Coordinate Punti Di Contatto Tra Parabola Asse Verticale E Circonferenza




Unit Circle




Equazione Della Circonferenza
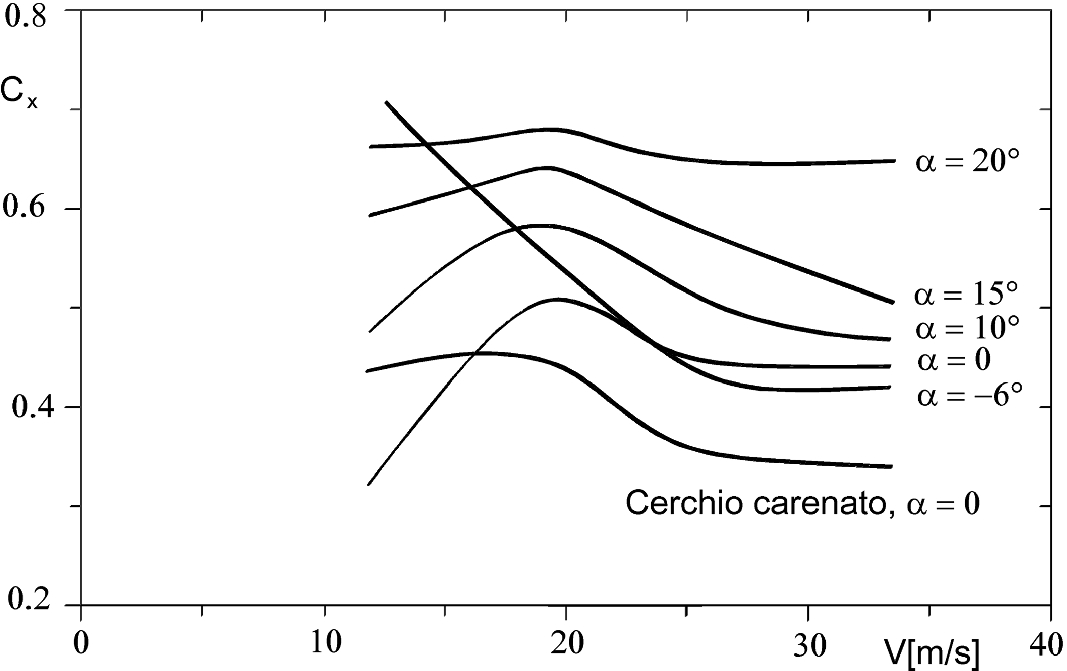



An Overview On Motor Vehicle Aerodynamics Springerlink




Circonferenza Equazione E Rappresentazione Nel Piano Cartesiano Youtube



Cerchio Di Superficie Doppia Geogebra
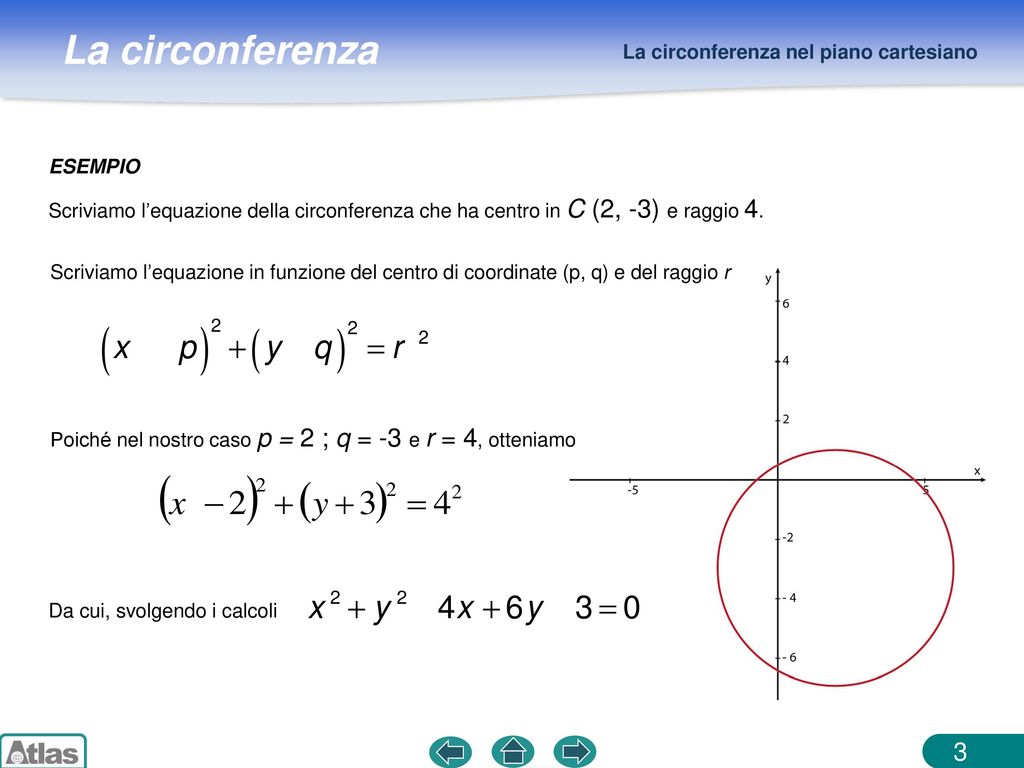



La Circonferenza Nel Piano Cartesiano Ppt Scaricare




A Generalized Power Law Detection Algorithm For Humpback Whale Vocalizations The Journal Of The Acoustical Society Of America Vol 131 No 4




Come Calcolare La Distanza 8 Passaggi Con Immagini



1




3 Ways To Calculate The Diameter Of A Circle Wikihow
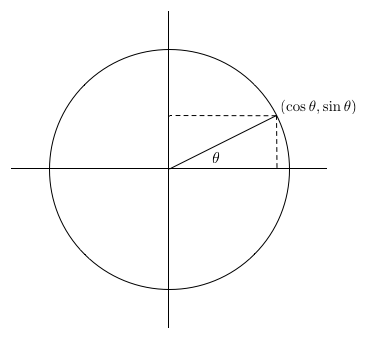



Tau Day No Really Pi Is Wrong The Tau Manifesto By Michael Hartl
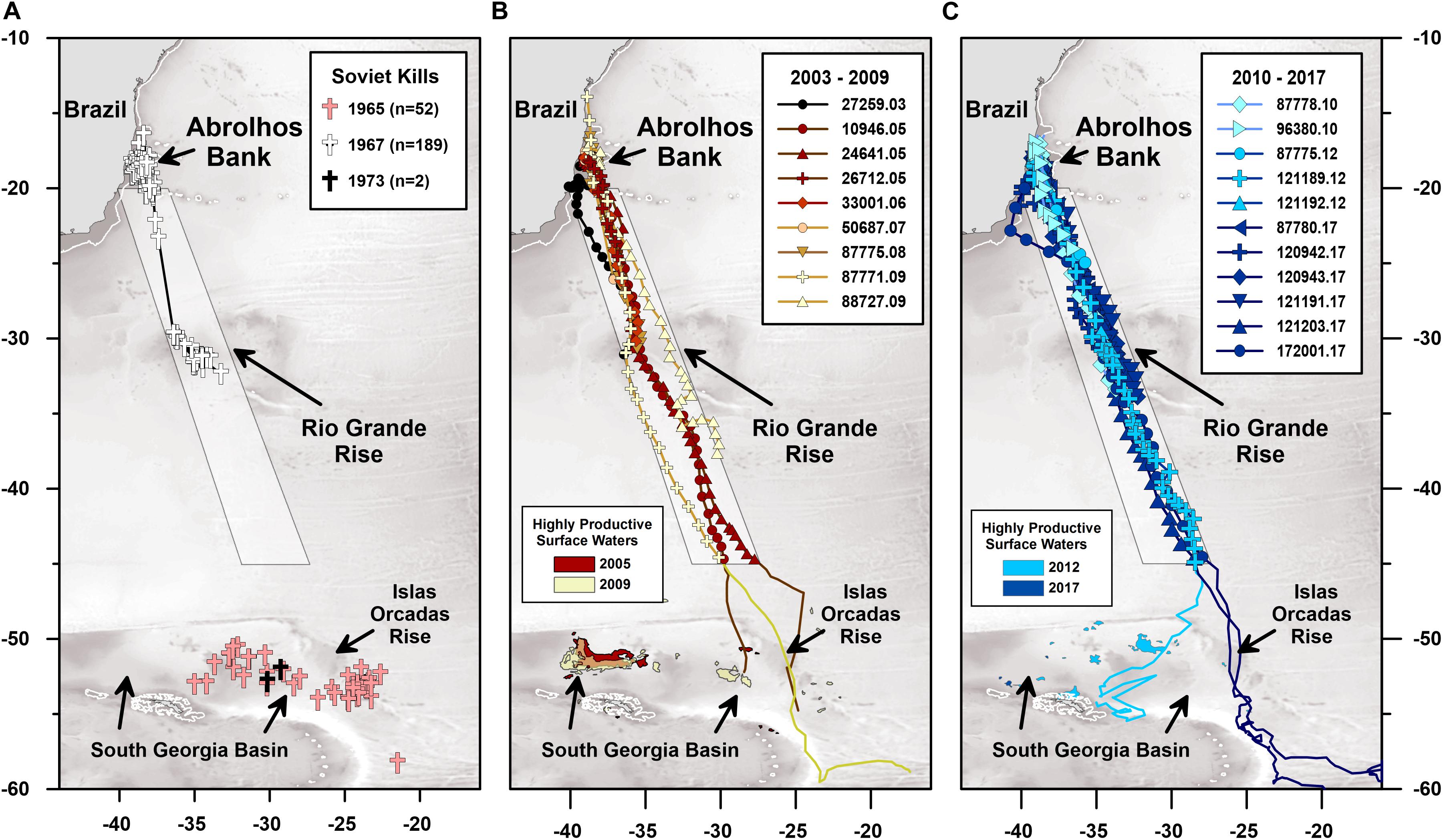



Frontiers Multi Decadal Humpback Whale Migratory Route Fidelity Despite Oceanographic And Geomagnetic Change Marine Science




Circonferenza E Cerchio Tutte Le Formule Redooc
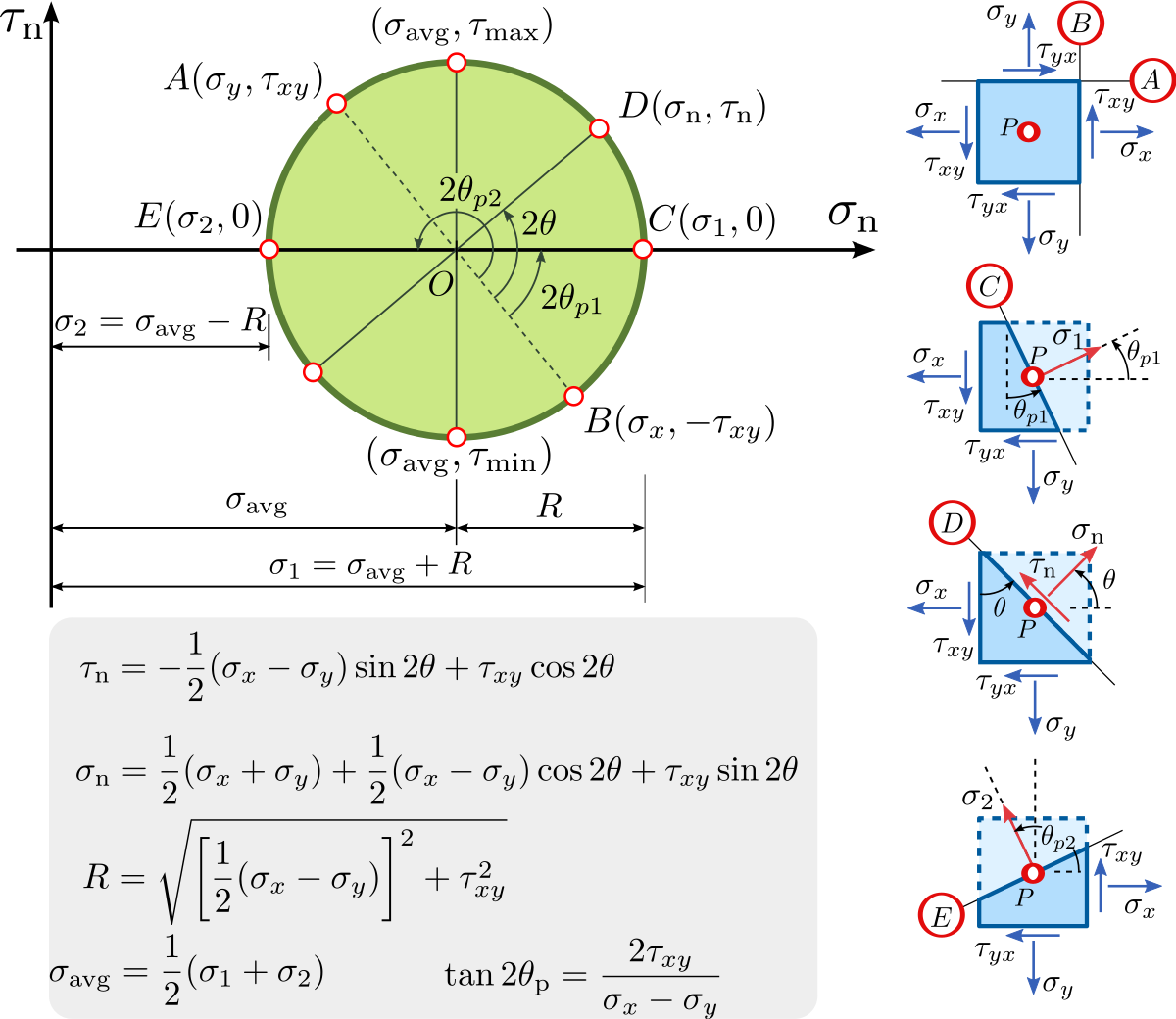



File Mohr Circle Plane Stress Angle Svg Wikimedia Commons




How To Find The Circumference And Area Of A Circle 14 Steps




Cillit Water Technology 2 Decals By Shlaps Community Gran Turismo Sport




X 2 Y 2 Formula X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Xy Yz Zx Formula Luar Biasa




Post Modern University Posts Facebook




Stratag An R Package For Manipulating Summarizing And Analysing Population Genetic Data Archer 17 Molecular Ecology Resources Wiley Online Library




How To Find The Circumference And Area Of A Circle 14 Steps



Circonferenza Con Excel



2




Parametric Equations



Equation Of A Circle



Hal Archives Ouvertes Fr Hal Document
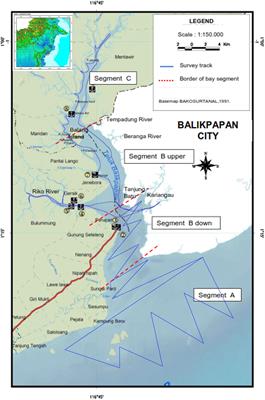



Frontiers Long Term Population And Distribution Dynamics Of An Endangered Irrawaddy Dolphin Population In Balikpapan Bay Indonesia In Response To Coastal Development Marine Science




Genetic Variation And Evidence For Population Structure In Eastern North Pacific False Killer Whales Pseudorca Crassidens




Lineaeffe 21 En By Oleg Kadnikov Issuu




Bioinformatica Paolo Maccallini



Www Naplesgov Com Sites Default Files Fileattachments Purchasing Page 18 008 Fire Station 1 Construction Addendum 5 Pdf



No comments:
Post a Comment